Here is a diophantine equation for me and Chris and whoever else is interested to practice on:
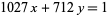
Here is the solution - but can we reproduce it with minimal cheating? Maybe Chris can solve it a less conventional way. He is pretty tricky like that. :))
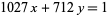
(gcd = greatest common divisor)
1. There is only a solution when gcd( 1027, 712 ) = 1 or in other words 1027 and 712 are relatively prime.
2. Using the Euclidian algorithm to calcutate gcd(1027,712)
$$\small{
\begin{array}{|r|r|r|r|}
\hline
&&&\\
a & b & q& r \\
\hline
&&&\\
1027 & 712 & 1 & 315 \\
712 & 315 & 2 & 82 \\
315 & 82 & 3 & 69 \\
82 & 69 & 1 & 13 \\
69 & 13 & 5 &4 \\
13 & 4 &3 & \textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{1} \\
4 & 1 & 4 & 0 \\
&&&\\
\hline
\end{array}
}$$
The greatest common divisor gcd(1027,712) $$\textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{=1}$$
and we can go on
3. Using Extended Euclidean algorithm to calculate the first solution
$$\small{
\begin{array}{|r|r|r|r||r|r|}
\hline
&&&&&\\
a & b & q& r &x&y\\
\hline
&&&&&\\
1027 & 712 & 1 & 315 & \textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{-165} & 73 - 1 (-165) = \textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{238}\\
712 & 315 & 2 & 82 & 73 & -19 - 2\cdot 73 = -165\\
315 & 82 & 3 & 69 & -19 & 16 -3(-19) = 73\\
82 & 69 & 1 & 13 & 16 & -3 -1\cdot 16 = -19\\
69 & 13 & 5 &4 & - 3 & 1 -5(-3) = 16\\
13 & 4 &3 & 1 & 1 & 0 - 3\cdot 1 = -3 \\
4 & 1 & 4 & 0 & 0 & 0\cdot 4 + 1 = 1\\
&&&&&\\
\hline
\end{array}
}$$
$$\small{\text{
The first solution is $ (-165,238) \qquad 1027 \cdot (\textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{ -165} ) + 712 \cdot \textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{238} = 1
$}}\\\\$$
4. All Solutions:
$$\small{\text{$
\begin{array}{lcl}
\boxed{
a\cdot x + b \cdot y = 1 }\\\\
\mathrm{First~ solution~~} (x_0,~ y_0)\\
\mathrm{All~ solutions~~} \left(x_0+\dfrac{z\cdot b}{ gcd(a,b) } ,~ y_0 - \dfrac{z\cdot a}{ gcd(a,b) }\right)\\
\end{array}
$}}\\\\$$
$$\small{\text{$
\begin{array}{lcl}
\boxed{
1027\cdot x + 712 \cdot y = 1 }\\\\
\mathrm{First~ solution~~} (x_0=-165,~ y_0=238)\\
\mathrm{All~ solutions~~} \left(-165+\dfrac{z\cdot 712}{ 1 } ,~ 238 - \dfrac{z\cdot 1027}{ 1 }\right)\\
\end{array}
$}}\\\\$$
we have:
$$\small{\text{$
\begin{array}{lcl}
\left\{~\left(~ -165 + 712\cdot z,~ 238 - 1027\cdot z\right)~|~z \in Z ~
\right\} \\
\end{array}
$}}\\\\$$
![]()
I'm going to employ maximum cheating on this one.......
Using the Euclidian algorithm, we have
1027 = 1(712) + 315
712 = 2(315) + 82
315 = 3(82) + 69
82 = 1(69) + 13
69 = 5(13) + 4
13 = 3(4) + 1
4 = 4(1) + 0
1 2 3 1 5 3 4
1 0 1 2 7 9 52 165 712
0 1 1 3 10 13 75 238 1027
Take the determinant of 165 712
238 1027 = -1
So.....
1027(165) - 712(238) = - 1 but...we need a "+1 " .....so......multiplying through by -1, we have
1027(-165) + 712(238) = 1
So....x = -165 and y = 238....however.....this is only one solution.....the general solution is given by
x , y = [ (-165 + 712k), (238 - 1027k) ]
![]()
![]()
![]()
Well....Ms. SmartyPants......I even provided a general solution.....so.....take that !!!

![]()
![]()
![]()
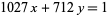
(gcd = greatest common divisor)
1. There is only a solution when gcd( 1027, 712 ) = 1 or in other words 1027 and 712 are relatively prime.
2. Using the Euclidian algorithm to calcutate gcd(1027,712)
$$\small{
\begin{array}{|r|r|r|r|}
\hline
&&&\\
a & b & q& r \\
\hline
&&&\\
1027 & 712 & 1 & 315 \\
712 & 315 & 2 & 82 \\
315 & 82 & 3 & 69 \\
82 & 69 & 1 & 13 \\
69 & 13 & 5 &4 \\
13 & 4 &3 & \textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{1} \\
4 & 1 & 4 & 0 \\
&&&\\
\hline
\end{array}
}$$
The greatest common divisor gcd(1027,712) $$\textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{=1}$$
and we can go on
3. Using Extended Euclidean algorithm to calculate the first solution
$$\small{
\begin{array}{|r|r|r|r||r|r|}
\hline
&&&&&\\
a & b & q& r &x&y\\
\hline
&&&&&\\
1027 & 712 & 1 & 315 & \textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{-165} & 73 - 1 (-165) = \textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{238}\\
712 & 315 & 2 & 82 & 73 & -19 - 2\cdot 73 = -165\\
315 & 82 & 3 & 69 & -19 & 16 -3(-19) = 73\\
82 & 69 & 1 & 13 & 16 & -3 -1\cdot 16 = -19\\
69 & 13 & 5 &4 & - 3 & 1 -5(-3) = 16\\
13 & 4 &3 & 1 & 1 & 0 - 3\cdot 1 = -3 \\
4 & 1 & 4 & 0 & 0 & 0\cdot 4 + 1 = 1\\
&&&&&\\
\hline
\end{array}
}$$
$$\small{\text{
The first solution is $ (-165,238) \qquad 1027 \cdot (\textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{ -165} ) + 712 \cdot \textcolor[rgb]{1,0,0}{238} = 1
$}}\\\\$$
4. All Solutions:
$$\small{\text{$
\begin{array}{lcl}
\boxed{
a\cdot x + b \cdot y = 1 }\\\\
\mathrm{First~ solution~~} (x_0,~ y_0)\\
\mathrm{All~ solutions~~} \left(x_0+\dfrac{z\cdot b}{ gcd(a,b) } ,~ y_0 - \dfrac{z\cdot a}{ gcd(a,b) }\right)\\
\end{array}
$}}\\\\$$
$$\small{\text{$
\begin{array}{lcl}
\boxed{
1027\cdot x + 712 \cdot y = 1 }\\\\
\mathrm{First~ solution~~} (x_0=-165,~ y_0=238)\\
\mathrm{All~ solutions~~} \left(-165+\dfrac{z\cdot 712}{ 1 } ,~ 238 - \dfrac{z\cdot 1027}{ 1 }\right)\\
\end{array}
$}}\\\\$$
we have:
$$\small{\text{$
\begin{array}{lcl}
\left\{~\left(~ -165 + 712\cdot z,~ 238 - 1027\cdot z\right)~|~z \in Z ~
\right\} \\
\end{array}
$}}\\\\$$
![]()