homework questions
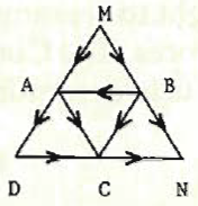
Using only the paths and directions shown, how many different routes are there from M to N?
Adjacency matrix directed: Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adjacency_matrix
If A is the adjacency matrix of the directed or undirected graph G,
then the matrix A^n (i.e., the matrix product of n copies of A) has an interesting interpretation:
the element (i, j) gives the number of (directed or undirected) walks of length n from vertex i to vertex j.
\(A = \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & M & A & B & D & C & N \\ \hline M & 0 & 1 & 1 & 0 & 0& \color{red}0 \\ \hline A & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 1& 0 \\ \hline B & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 1& 1 \\ \hline D & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1& 0 \\ \hline C & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0& 1 \\ \hline N & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0& 0 \\ \hline \end{array} ~\text{There is $0\times$ 1-way route }\)
\(A^2 = \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & M & A & B & D & C & N \\ \hline M & 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 2 & \color{red}1 \\ \hline A & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline B & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline D & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline C & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline N & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline \end{array} ~\text{There is $1\times$ 2-way route }\)
\(A^3 = \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & M & A & B & D & C & N \\ \hline M & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 2 & \color{red}2 \\ \hline A & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline B & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline D & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline C & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline N & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline \end{array} ~\text{There are $2\times$ 3-way routes }\)
\(A^4 = \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & M & A & B & D & C & N \\ \hline M & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & \color{red}2 \\ \hline A & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline B & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline D & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline C & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline N & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline \end{array} ~\text{There are $2\times$ 4-way routes }\)
\(A^5 = \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & M & A & B & D & C & N \\ \hline M & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \color{red}1 \\ \hline A & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline B & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline D & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline C & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline N & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline \end{array} ~\text{There is $1\times$ 5-way route }\)
\(A^6 = \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & M & A & B & D & C & N \\ \hline M & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \color{red}0 \\ \hline A & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline B & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline D & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline C & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline N & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\ \hline \end{array} ~\text{There is $0\times$ 6-way routes }\)
1+2+2+1 = 6 different routes are there from M to N
![]()
Suppose that f is a Mobius transformation such that \(f(1)=i\), \(f(i)=-1\), and \(f(-1)=1\).
Find the value of \(f(-i)\).
Möbius transformation: \(w={\dfrac {az+b}{cz+d}}\) of one complex variable z; here the coefficients a, b, c, d are complex number.
\( a=\det {\begin{pmatrix}z_{1}w_{1}&w_{1}&1\\z_{2}w_{2}&w_{2}&1\\z_{3}w_{3}&w_{3}&1\end{pmatrix}}\, \\ b=\det {\begin{pmatrix}z_{1}w_{1}&z_{1}&w_{1}\\z_{2}w_{2}&z_{2}&w_{2}\\z_{3}w_{3}&z_{3}&w_{3}\end{pmatrix}}\, \\ c=\det {\begin{pmatrix}z_{1}&w_{1}&1\\z_{2}&w_{2}&1\\z_{3}&w_{3}&1\end{pmatrix}}\, \\ d=\det {\begin{pmatrix}z_{1}w_{1}&z_{1}&1\\z_{2}w_{2}&z_{2}&1\\z_{3}w_{3}&z_{3}&1\end{pmatrix}}\)
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/M%C3%B6bius_transformation
\(\begin{array}{|rll|} \hline f(z)=w \\ \hline f(1)=i: & z_1=1 & w_1 =i \\ f(i)=-1: & z_2=i & w_2 = -1 \\ f(-1)=1: & z_3=-1 & w_3 = 1 \\ \hline \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{|lcll|} \hline a= \begin{vmatrix}i&i&1\\-i&-1&1\\-1&1&1\end{vmatrix}&=& -4i-2 \\\\ b= \begin{vmatrix}i&1&i\\-i&i&-1\\-1&-1&1\end{vmatrix}&=& -2 \\\\ c= \begin{vmatrix}1&i&1\\i&-1&1\\-1&1&1\end{vmatrix}&=& -2 \\\\ d= \begin{vmatrix}i&1&1\\-i&i&1\\-1&-1&1\end{vmatrix}&=& 4i-2 \\ \hline \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{|rll|} \hline f(z)=w &=& \dfrac {az+b}{cz+d} \\\\ \mathbf{f(z)} &=& \mathbf{\dfrac {(-4i-2)z-2}{(-2)z+(4i-2)}} \\ \hline \\ f(-i) &=& \dfrac {(-4i-2)(-i)-2}{(-2)(-i)+(4i-2)} \\\\ &=& \dfrac {4i^2+2i-2}{2i+4i-2} \quad | \quad i^2 = -1 \\\\ &=& \dfrac {-4+2i-2}{6i-2} \\\\ &=& \dfrac { 2i-6}{6i-2} \\\\ &=& \dfrac { 2(i-3)}{2(3i-1)} \\\\ &=& \dfrac { (i-3)}{ (3i-1)}*\dfrac{(3i+1)}{(3i+1)} \\\\ &=& \dfrac {3i^2+i-9i-3}{9i^2-1} \\\\ &=& \dfrac {-3+i-9i-3}{-9-1} \\\\ &=& \dfrac {-6-8i}{-10} \\\\ &=& \dfrac {6+8i}{10} \\\\ &=& \dfrac {6}{10} +\dfrac {8}{10}i \\\\ \mathbf{f(-i)} &=& \mathbf{0.6+0.8i} \\ \hline \end{array}\)
![]()