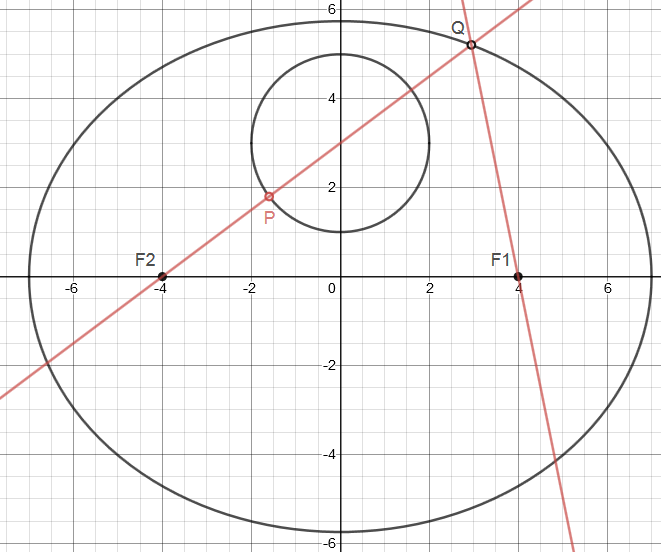
The foci of the ellipse\( \dfrac{x^2}{49} + \dfrac{y^2}{33} = 1\) are \(F_1\) and \(F_2\) as shown below.
Let P be a point on the circle \(x^2 + (y - 3)^2 = 4\).
Line \(F_2P\) intersects the ellipse again at Q,
where the y-coordinate of Q is positive.
Find the maximum value of \(PQ + F_1 Q\).
\(\text{1. Parameter of the ellipse:}\\ \begin{array}{rcll} a^2 &=& 49 \\ \mathbf{a} &=& \mathbf{7} \\\\ \mathbf{b^2} &=& \mathbf{33} \\\\ c^2 &=& a^2-b^2 \\ c^2 &=& 49-33\\ c^2 &=& 16 \\ \mathbf{c} &=& \pm4 \\\\ F_2 &=& (-c,0) = (-4,0) \\ F_1 &=& (c,0) = (4,0) \\ \end{array}\)
\(\text{2. Find the maximum value:}\\ \begin{array}{|rcll|} \hline (PQ + F_1 Q)_{max} &=& F_2Q+F_1Q-F_2P \quad | \quad F_1Q+F_2P = 2a \\ (PQ + F_1 Q)_{max} &=& 2a-F_2P \quad | \quad a=7 \\ (PQ + F_1 Q)_{max} &=& 14-F_2P \\ && F_2P= \sqrt{(x_p-(-4))^2+(y_p-0)^2} \\ && \mathbf{F_2P= \sqrt{(x_p+4)^2+y_p^2}} \\ && \boxed{x_p^2+(y_p-3)^2=4\\ (y_p-3)^2=4-x_p^2 \\ \mathbf{y_p=3+\sqrt{4-x_p^2} } \\ \ldots \\ y_p^2 = 13-x_p^2 +6\sqrt{4-x_p^2} } \\ && F_2P= \sqrt{(x_p+4)^2+13-x_p^2 +6\sqrt{4-x_p^2}} \\ && F_2P= \sqrt{x_p^2+8x_p+16+13-x_p^2 +6\sqrt{4-x_p^2}} \\ && F_2P= \sqrt{29+8x_p+6\sqrt{4-x_p^2}} \\ (PQ + F_1 Q)_{max} &=& 14-\sqrt{29+8x_p+6\sqrt{4-x_p^2}} \\\\ (PQ + F_1 Q)_{max} &=& 14-( 29+8x_p+6(4-x_p^2)^{\frac12} )^{\frac12} \\\\ \text{derivation:} \\ && \boxed{-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(29+8x_p+6(4-x_p^2)^{\frac12} \right)^{\frac12-1} \\ \times \left(8+\dfrac{6}{2}(4-x_p^2)^{\frac12-1}(-2x_p) \right)} \\\\ \text{derivation $= 0$:} \\ && -\dfrac{8-\dfrac{6x_p}{\sqrt{4-x_p^2}} } {2\sqrt{29+8x_p+6\sqrt{4-x_p^2} } } = 0 \\\\ && 8-\dfrac{6x_p}{\sqrt{4-x_p^2}} = 0 \quad | \quad : 2 \\\\ && 4-\dfrac{3x_p}{\sqrt{4-x_p^2}} = 0 \\\\ && \dfrac{3x_p}{\sqrt{4-x_p^2}} = 4 \\\\ && 3x_p = 4\sqrt{4-x_p^2} \quad | \quad \text{square both sides} \\ && 9x_p^2 = 16(4-x_p^2) \\ && 9x_p^2 = 64-16x_p^2 \\ && \ldots \\ && \mathbf{x_p} = \pm\dfrac{8}{5} \\ \hline \end{array}\)
\(\begin{array}{|rcll|} \hline y_p &=& 3\pm \sqrt{4-x_p^2} \quad | \quad x_p = \pm\dfrac{8}{5} \\ \ldots \\ y_p &=& 3\pm\dfrac{6}{5} \\\\ \mathbf{y_p= \dfrac{21}{5} } &\text{or}&\mathbf{y_p= \dfrac{9}{5} } \\ \hline \end{array}\)
\(\begin{array}{|lrcll|} \hline x_p=\dfrac{8}{5},~y_p=\dfrac{9}{5}: & F_2P &=& \sqrt{ \left(\dfrac{8}{5}+4\right)^2 + \left(\dfrac{9}{5}\right)^2 } \\ & F_2P &=& \dfrac{ \sqrt{28^2+9^2 } } {5} \\ & \mathbf{F_2P} &=& \mathbf{5.8821764679} \\ \hline x_p=\dfrac{8}{5},~y_p=\dfrac{21}{5}: & F_2P &=& \sqrt{ \left(\dfrac{8}{5}+4\right)^2 + \left(\dfrac{21}{5}\right)^2 } \\ & F_2P &=& \dfrac{ \sqrt{28^2+21^2 } } {5} \\ & \mathbf{F_2P} &=& \mathbf{7} \\ \hline x_p=-\dfrac{8}{5},~y_p=\dfrac{9}{5}: & F_2P &=& \sqrt{ \left(-\dfrac{8}{5}+4\right)^2 + \left(\dfrac{9}{5}\right)^2 } \\ & F_2P &=& \dfrac{ \sqrt{12^2+9^2 } } {5} \\ & \mathbf{F_2P} &=& \mathbf{3} \\ \hline x_p=-\dfrac{8}{5},~y_p=\dfrac{21}{5}: & F_2P &=& \sqrt{ \left(-\dfrac{8}{5}+4\right)^2 + \left(\dfrac{21}{5}\right)^2 } \\ & F_2P &=& \dfrac{ \sqrt{12^2+21^2 } } {5} \\ & \mathbf{F_2P} &=& \mathbf{4.8373546490} \\ \hline \end{array}\)
\(\text{For the maximum we need the smallest value of $F_2P$: $\quad F_2P = 3$ }\\ \begin{array}{|rcll|} \hline (PQ + F_1 Q)_{max} &=& 14-F_2P \\ (PQ + F_1 Q)_{max} &=& 14-3 \\ \mathbf{(PQ + F_1 Q)_{max}} &=& \mathbf{11} \\ \hline \end{array}\)
