(a)
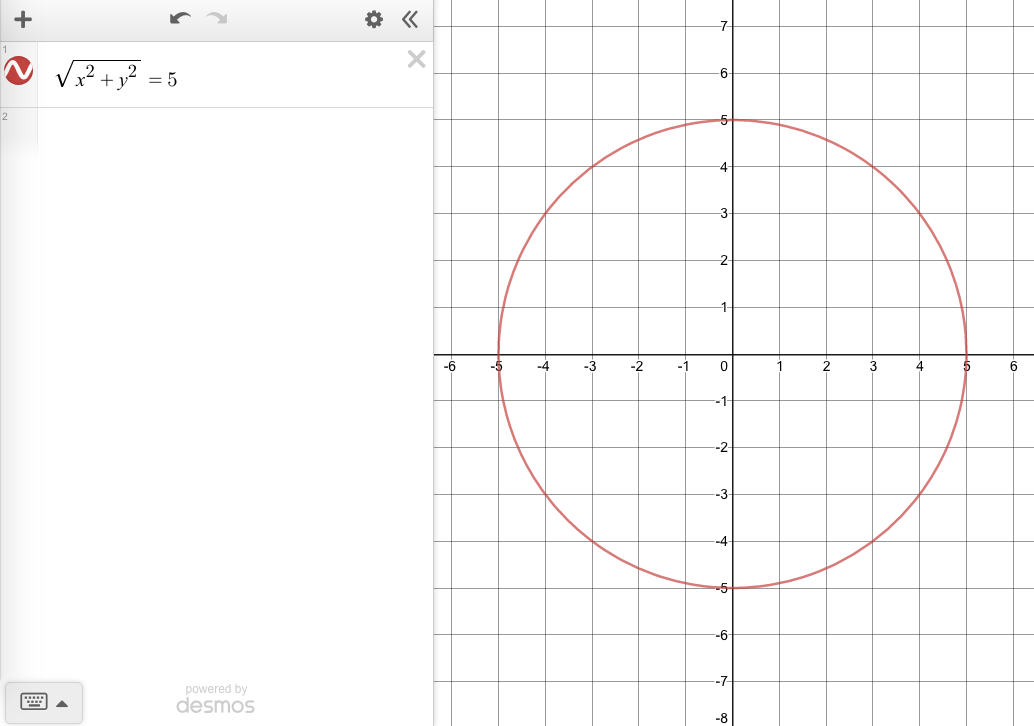
\(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\ =\ 5\)
The solutions to this equation are all points with a distance of 5 from the origin.
So this is the equation of a circle with a radius of 5 centered at the origin.
I used a little help from here: https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/518856/integral-points-on-a-circle
There is a Pythaogrean triple with a hypotenuse of 5
A triangle with side lengths 3, 4 and 5 is a Pythagorean triple. So...
From the origin, we can go over 3 units and either up or down 4 units to reach an integer solution.
From the origin, we can go over 4 units and either up or down 3 units to reach an integer solution.
From the origin, we can go over 0 units and either up or down 5 units to reach an integer solution.
From the origin, we can go over 5 units and either up or down 0 units to reach an integer solution.
Here's a graph showing all integer solutions: https://www.desmos.com/calculator/txwzj5nmt4
There are 12 integer solutions.
\(0 \ >\ \dfrac{1}{1-\frac{10}{x}}\ >\ 1 - \dfrac{5}{y}\)
So...
\(\dfrac{1}{1-\frac{10}{x}}\ >\ 1 - \dfrac{5}{y}\\~\\~\\ \dfrac{x}{x-10}\ >\ 1 - \dfrac{5}{y}\\~\\~\\ \dfrac{x}{x-10}-1\ >\ - \dfrac{5}{y}\\~\\~\\ \dfrac{x}{x-10}-\dfrac{x-10}{x-10}\ >\ - \dfrac{5}{y}\\~\\~\\ \dfrac{10}{x-10}\ >\ -\dfrac5y\)
And we know 0 < x < 10 because that is the only way \(\dfrac{1}{1-\frac{10}{x}}\) can be less than 0.
So x - 10 is negative, and so when we multiply both sides by (x - 10) , flip the sign.
\(10\ <\ -\dfrac5y(x-10)\)
And we know 0 < y < 5 because that is the only way \(1-\dfrac5y\) can be less than 0.
So y is positive, and so when we multiply both sides by y , don't flip the sign.
\(10y\ <\ -5(x-10)\\~\\ y\ <\ -\frac12(x-10)\\~\\ y\ <\ -\frac12x+5\)
And so we have these three inequalities:
\(1.\qquad0\ {<}\ x\ {<}\ 10\\~\\ 2.\qquad0\ {<}\ y\ {<}\ 5\\~\\ 3.\qquad y\ {<}\ -\frac12x+5\)
We can see on a graph that the intersection of these is a triangle:
https://www.desmos.com/calculator/2xloyva03v
All the points that lie within the shaded triangle are solutions to the inequality.
And we can see there are 16 pairs of integers (x, y) that satisfy the inequality.