Find a polynomial $f(x)$ of degree $5$ such that both of these properties hold:
$f(x)-1$ is divisible by $(x-1)^3$.
$f(x)$ is divisible by $x^3$.
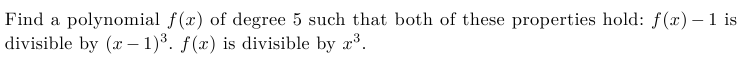
1. \(\bf{\text{ $\mathbf{f(x)}$ is divisible by $\mathbf{x^3}~$ ?}}\)
\(\begin{array}{lcll} \text{Let $f(x) = a(x-x_1)(x-x_2)(x-x_3)(x-x_4)(x-x_5)$ is a polynomial of degree $5$.} \\ \text{If f(x) is divisible by $x^3$, than $x_1=x_2=x_3=0 $} \\ \qquad f(x) = a(x-0)(x-0)(x-0)(x-x_4)(x-x_5) \\ \qquad \boxed{f(x) =ax^3(x-x_4)(x-x_5)} \text{ This polynom is divisible by $x^3$} \\ \text{expand to:} \\ \qquad f(x)= ax^5 - a(x_4+x_5)x^4 + ax_4x_5x^3 \qquad \text{Let $A=a$, $~B=a(x_4+x_5)$, and $~C = ax_4x_5 $ } \\ \text{finally we have:} \\ \qquad \boxed{f(x) = Ax^5+Bx^4+Cx^3 \qquad (1) } \text{ This polynom is divisible by $x^3$} \\ \end{array}\)
2. \(\bf{\text{ $\mathbf{f(x)-1}$ is divisible by $\mathbf{(x-1)^3}~$ ?}}\)
\(\begin{array}{lcll} \text{Say $P(x) $ is a polynom divisible by $(x-1)^3$ .} \\ \text{Set:}\\ \qquad P(x)=b\cdot(x-1)^3 \\ \qquad \text{The root is $x = 1$ }\\ \text{so}\\ \qquad P(1)=b(1-1)^3=0 \\ \text{Set also:}\\ \qquad \text{ $P'(x)= 3b(x-1)^2 $}\\ \text{so}\\ \qquad P'(1)= 3b(1-1)^2=0 \\ \text{Set finally:}\\ \qquad \text{ $P''(x)= 6b(x-1) $}\\ \text{so}\\ \qquad P''(1)= 6b(1-1)^2=0 \\\\ \text{Conclusion} \\ \text{If $P(x)$ is divisible by $(x-1)^3$, so $\boxed{\mathbf{P(1)=P'(1)=P''(1)=0}\qquad (2)}$ at the root $x=1$ } \\ \end{array}\)
\(\begin{array}{lrcll} \text{We set:}\\ \text{1)}& f(x) - 1 &=& P(x) \quad & | \quad \text{$f(x)-1$ and $P(x)$ are divisible by $(x-1)^3 $ }\\ & f(1) -1 &=& P(1) = 0 \quad & | \quad \rightarrow (2) \\\\ \text{2)}& (f(x) - 1)' &=& P'(x) \\ & f'(x) &=& P'(x) \\ & f'(1) &=& P'(1) = 0 \quad & | \quad \rightarrow (2) \\\\ \text{3)}& (f(x) - 1)'' &=& P''(x) \\ & f''(x) &=& P''(x) \\ & f''(1) &=& P''(1) = 0 \quad & | \quad \rightarrow (2) \\ \end{array}\)
\(\begin{array}{lrcll} \text{We see:}\\ & \boxed{ \begin{array}{r} f(1) -1 = 0 \qquad (3) \\ f'(1) = 0 \qquad (4) \\ f''(1)= 0 \qquad (5) \\ \end{array} } \end{array}\)
\(\begin{array}{lrcll} \text{We calculate:}\\ & f(x) &=& Ax^5+Bx^4+Cx^3 \\ & f(x) -1 &=& Ax^5+Bx^4+Cx^3 - 1 \\ & f(1)-1 &=& A+B+C -1 = 0 \quad & | \quad \rightarrow (3) \\\\ & f'(x) &=& 5Ax^4+4Bx^3+3Cx^2 \\ & f'(1) &=& 5A+4B+3C = 0 \quad & | \quad \rightarrow (4) \\\\ & f''(x) &=& 20Ax^3+12Bx^2+6Cx \\ & f''(1) &=& 20A+12B+6C = 0 \quad & | \quad \rightarrow (5) \\ \end{array}\)
\(\begin{array}{lrcll} \text{Solve the Simultaneous Equations, we calculate $A~$, $B~$, $C~$ :} \\ \end{array}\\ \begin{array}{lrcll} A+B+C -1 = 0 \quad \Rightarrow & A+B+C &=& 1 \\ & 5A+4B+3C &=& 0 \\ & 20A+12B+6C &=& 0 \\ \end{array}\)
Cramer's Rule:
\(\begin{array}{rcrcrcr} 1\cdot A &+& 1\cdot B &+& 1\cdot C &=& 1 \\ 5\cdot A &+& 4\cdot B &+& 3\cdot C &=& 0 \\ 20\cdot A &+& 12\cdot B &+& 6\cdot C &=& 0 \\ \end{array}\\ \small{ \begin{array}{lcl} \\ \text{Determinant denominator} &=& \begin{vmatrix} 1&1&1 \\ 5&4&3 \\ 20&12&6 \\ \end{vmatrix}\\ \\ &=& 1\cdot 4\cdot 6 + 5\cdot 12\cdot 1 +20\cdot 1\cdot 3 - 20\cdot 4\cdot 1 -1\cdot 12\cdot 3 -5\cdot 1\cdot 6\\ &=& 24+60+60-80-36-30 \\ &=& -2 \\ \end{array} } \)
\(\begin{array}{lcl} A &=& \dfrac{ \begin{vmatrix} 1&1&1 \\ 0&4&3 \\ 0&12&6 \\ \end{vmatrix} }{-2}\\\\ &=&\dfrac{ 1\cdot 4\cdot 6 - 1\cdot 12\cdot 3 } {-2}\\ &=&\dfrac{ -12 } {-2}\\\\ \mathbf{A} & \mathbf{=} & \mathbf{6}\\ \end{array} \begin{array}{lcl} B &=& \dfrac{ \begin{vmatrix} 1&1&1 \\ 5&0&3 \\ 20&0&6 \\ \end{vmatrix} }{-2}\\\\ &=&\dfrac{ 20\cdot 1\cdot 3 - 5\cdot 1\cdot 6 } {-2}\\ &=&\dfrac{ 30 } {-2}\\\\ \mathbf{B} & \mathbf{=} & \mathbf{-15}\\ \end{array} \begin{array}{lcl} C &=& \dfrac{ \begin{vmatrix} 1&1&1 \\ 5&4&0 \\ 20&12&0 \\ \end{vmatrix} }{-2}\\\\ &=&\dfrac{ 5\cdot 12\cdot 1 - 20\cdot 4\cdot 1 } {-2}\\ &=&\dfrac{ -20 } {-2}\\\\ \mathbf{C} & \mathbf{=} & \mathbf{10}\\ \end{array}\)
\(\begin{array}{lrcll} \text{The Polynom $f(x) = Ax^5+Bx^4+Cx^3$ with $A=6$, $~B=-15$, and $~C = 10$}\\ \quad \boxed{f(x)=6x^5-15x^4+10x^3} \end{array}\)
Proof:
\(\begin{array}{|rcll|} \hline f(3) &=& 6\cdot 3^5-15\cdot 3^4 + 10 \cdot 3^3 \\ &=& 1458-1215+270 \\ &=& 513 \\ \frac{f(3)}{3^3} &=& \frac{513}{3^3} \\ &=& 19\ \checkmark \\ \frac{f(3)-1}{(3-1)^3} &=& \frac{513-1}{2^3} \\ &=& \frac{512}{8} \\ &=& 64\ \checkmark \\ \hline \end{array}\)
