If the roots of the quadratic equation \(\frac12x^2+99x+c=0 \) are \(x=-99+\sqrt{8001}\) and \(x=-99-\sqrt{8001},\) then what is the value of \(c\)?
| In the factored form of a quadratic equation: \((x-b)(x-c)=0\) | The two solutions are \(x_1=b;x_2=c\) |
| \([x-(-99-\sqrt{8001})][x-(-99+\sqrt{8001})]=0\) | We used the logic above the reach this conclusion. |
| \((x+99+\sqrt{8001})(x+99-\sqrt{8001})=0\) | Simplifying |
| \(x^2+198x+1800=0\) | Finalizing |
| \(\frac12x^2+99x+900=0 \) | Dividing by 2 to get the form the question presents |
\(c=\boxed{900}\)
I hope this helped,
Gavin
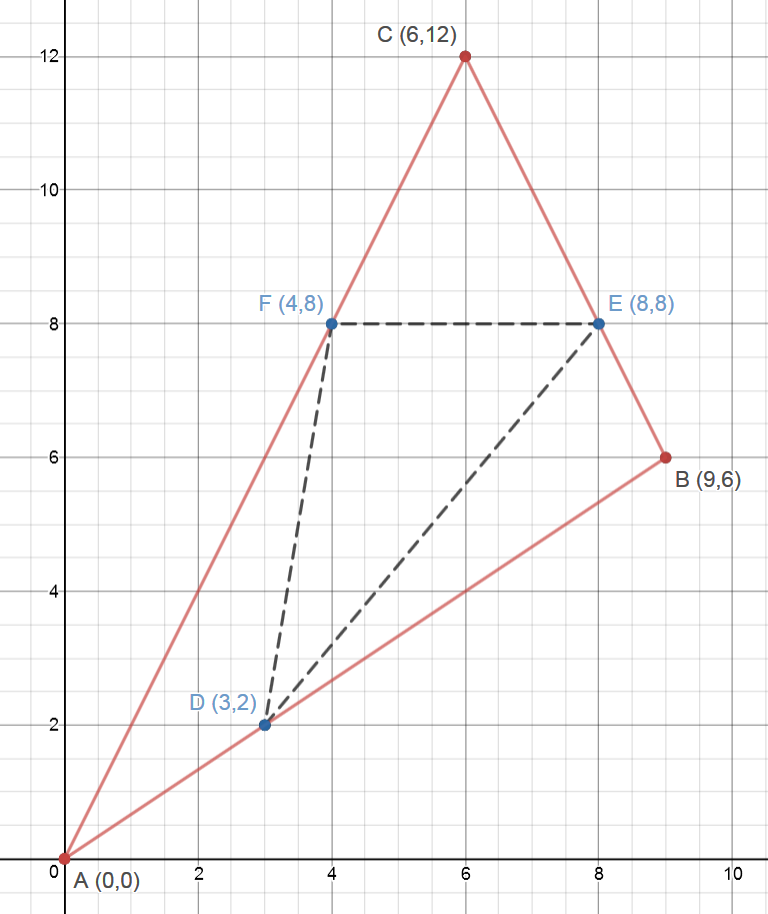
2: Points A(0,0), B(9,6) and C(6,12) are vertices of triangle ABC.
Point D is on segment AB such that 2(AD) = DB,
point E is on segment BC such that 2(BE) = EC and
point F is on segment CA such that 2(CF) = FA.
What is the ratio of the area of triangle DEF to the area of triangle ABC?
Express your answer as a common fraction.
\(\begin{array}{|rcll|} \hline D &=& \dbinom{9}{6}\cdot \dfrac13 \\ &=& \dbinom{3}{2} \\\\ E &=& \dbinom{9}{6} + \left( \dbinom{6}{12} - \dbinom{9}{6} \right)\cdot \dfrac13 \\ &=& \dbinom{9}{6} + \dbinom{-3}{6}\cdot \dfrac13 \\ &=& \dbinom{9}{6} + \dbinom{-1}{2} \\ &=& \dbinom{8}{8} \\\\ F &=& \dbinom{6}{12}\cdot \dfrac23 \\ &=& \dbinom{12}{24}\cdot \dfrac13 \\ &=& \dbinom{4}{8} \\ \hline \end{array} \\ \begin{array}{|rcll|} \hline \text{Area}_\text{ABC} &=& \frac12 \left( 0\cdot 6 - 9\cdot 0 + 9 \cdot 12 - 6 \cdot 6 + 6\cdot 0 - 0 \cdot 12 \right) \\ &=& \frac12 \left( 9 \cdot 12 - 6 \cdot 6 \right) \\ &=& \frac12 \left( 72 \right) \\ &=& 36 \\ \hline \end{array} \\ \begin{array}{|rcll|} \hline \text{Area}_\text{DEF} &=& \frac12 \left( 3\cdot 8 - 8 \cdot 2 + 8 \cdot 8 - 4 \cdot 8 + 4\cdot 2 - 3 \cdot 8 \right) \\ &=& \frac12 \left( 24-16+64-32+8-24 \right) \\ &=& \frac12 \left( 24 \right) \\ &=& 12 \\ \hline \end{array}\\ \begin{array}{|rcll|} \hline \dfrac { \text{Area}_\text{DEF} } {\text{Area}_\text{ABC}} &=& \dfrac{12}{36} = \dfrac13 \\ \hline \end{array}\)
Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0KjG8Pg6LGk
![]()